Few things frustrate an online seller more than having their Google Merchant Center account suspended for misrepresentation. It’s a common issue and what makes it even worse is that Google often doesn’t specify what the problem is. You’re left guessing, trying to figure out what went wrong while your products disappear from search, traffic drops off, and sales take a hit.
In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what the misrepresentation policy means, what the most common triggers are, and how to run a thorough audit of your store to find and fix violations. You’ll find step-by-step instructions based on real-world experience managing Merchant Center accounts, along with tips on meeting product-related requirements that can also impact your store’s compliance.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- Dealing with a Google Merchant Center Suspension for Misrepresentation
- How to Tell If Your Merchant Center Account Has Been Suspended
- Fix Your Google Merchant Center Suspension
- 12 of The Most Common Reasons Accounts Get Suspended
- Deep Dive: The most common Google Merchant Center Suspension Reasons Explained
- Product Ads Policies – What You Should Know
- Requesting a Review of Your Store by Google
- Solving the Google Merchant Center Misrepresentation Issue
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Final Thoughts: Google Merchant Center Misrepresentation Issue
Dealing with a Google Merchant Center Suspension for Misrepresentation
This issue tends to affect newly created accounts, but even well-established ones can get suspended. Whether you’re using a standard Google Shopping setup or working with a third-party CSS (Comparison Shopping Service), no account is completely safe from suspension.
For smaller, more straightforward issues, Google might tell you exactly what’s wrong — making it easier to fix Google Merchant Center suspension issues. But when it comes to more serious or complex violations, they usually don’t offer much detail. You won’t get a list of problematic products or specific feed errors, which makes diagnosing the problem a real challenge.
That’s where this guide comes in. We’ll walk you through the most common causes of suspension, help you identify potential issues on your site, and share practical tips to get your products visible to customers again.
How to Tell If Your Merchant Center Account Has Been Suspended
Before pulling the plug completely, Google often sends a warning and starts by limiting your product visibility. You might get an email or see a notification directly in your Merchant Center account. These alerts usually include a deadline for fixing the issues and submitting your account for review.
That said, in some cases, Google skips the warning and suspends the account right away if they spot a more serious policy violation.
To check your account status, just log into your Google Merchant Center dashboard — if there’s an issue, you’ll see a clear message letting you know your account is restricted or suspended.
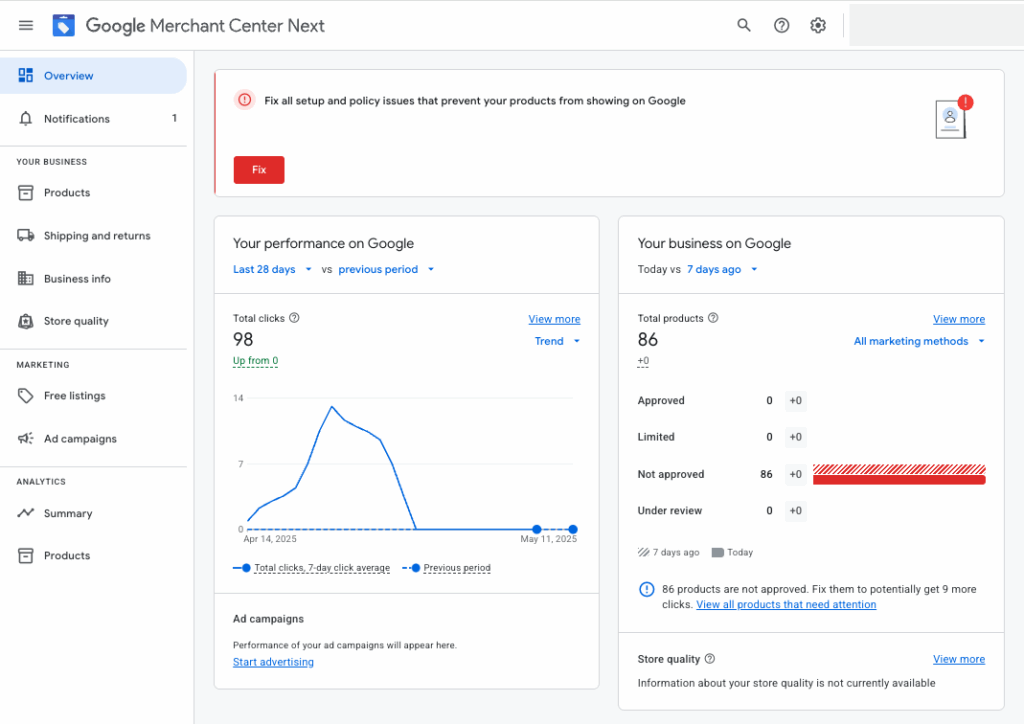
You’ll also be notified by email. Google sends a message to the address associated with your Merchant Center account.
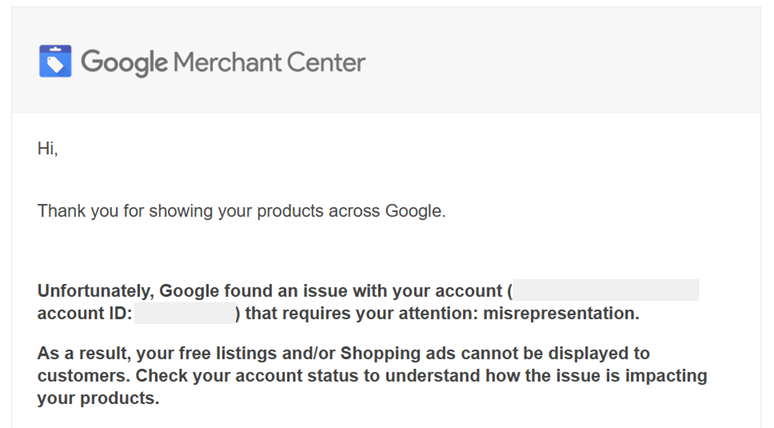
Notifications from Google often include guidance on how to fix the issue. However, the information provided can be quite general and may not specify exactly what needs to be corrected—just which requirements you should review.
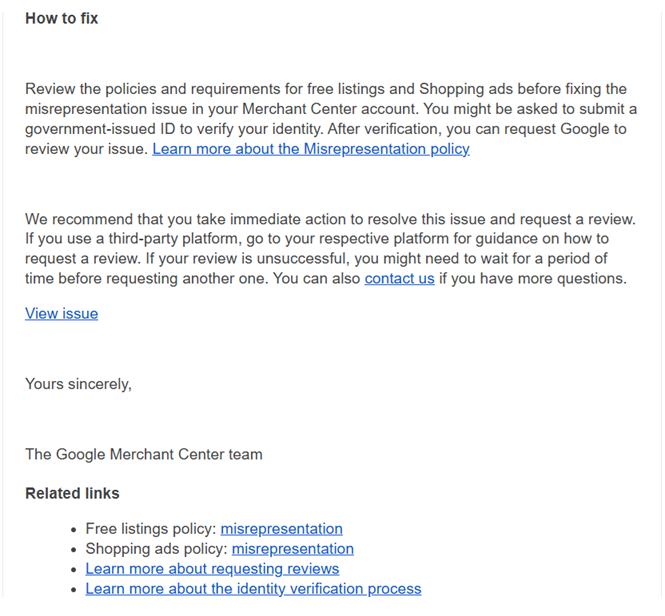
Fix Your Google Merchant Center Suspension
Google has a detailed set of policies designed to protect its users. One of the most common reasons for account suspension is a violation of its transparency guidelines — something Google labels as misrepresentation.
To fix a Google Merchant Center suspension, you’ll usually need to do a deep dive into your store, look at it from Google’s perspective, and ensure everything is in order before requesting a review.
Why was my Google Merchant Center account suspended for misrepresentation?
In Google Merchant Center, misrepresentation means providing misleading or inaccurate information about your products or business.
Here are 12 of the most common reasons accounts get suspended for misrepresentation:
- Price mismatch between Merchant Center and your website.
- Promotions that are no longer available.
- Inconsistent shipping costs or unclear delivery methods.
- Hidden or unexpected fees at checkout.
- Misleading product descriptions or exaggerated claims.
- Technical issues during checkout or payment.
- Missing or incorrectly implemented SSL certificates.
- Broken links or faulty website elements.
- Missing or incomplete contact and legal information.
- Mismatch between store name and registered business name.
- Non-compliance with legal requirements (e.g., Omnibus Directive, cookie consent)
- Language and currency inconsistencies.
Each of these areas includes specific elements that should be closely reviewed during a store audit. Even minor oversights can be flagged by Google as breaches of transparency.
In the next section, we’ll break down each issue in detail and highlight key points to watch for when reviewing your site.
Deep Dive: The Most Common Misrepresentation Reasons Explained
Getting your Google Merchant Center account suspended for misrepresentation typically means there are inconsistencies between what you tell users in your ads and what’s actually found on your website.
In other words, if the information you present to users isn’t fully accurate, clear, or transparent, Google may view your site as failing to meet its trust and transparency standards.
Below, we examine the most common reasons why Google may flag a store for failing to meet those standards:
1. Price Mismatch Between Merchant Center and Your Website
One of the most frequent issues is when the price shown in your product feed doesn’t match what users see on your landing page. This often happens with products that have multiple variants (e.g., drinks sold in 0.25L, 0.5L, and 1L bottles) where the price isn’t clearly linked to the specific variant or differs from the feed data.
How to fix it:
- Make sure every product variant has a clear and accurate price on the landing page.
- Keep your product feed regularly updated to reflect real-time prices.
- If you run a large store and fixing each issue is time-consuming, consider temporarily excluding problematic items using rules in Merchant Center or filters in your feed generation tool.
2. Promotions That Aren’t Actually Available
Ads promoting deals that no longer exist — like out-of-stock items, expired offers, or calls to action that can’t be followed through on the landing page — are a red flag.
To avoid this, regularly update your promotions and double-check that your landing page content matches what your ads are saying.
3. Inconsistent Shipping Costs or Unclear Delivery Methods
- If the shipping costs shown in your feed don’t match what’s shown during checkout, in your shipping policy, or on the product page, that’s a problem.
- Google expects you to offer at least one standard delivery method (like home delivery via courier), not just pickup options like lockers or collection points.
4. Hidden or Unexpected Charges
Extra fees that pop up during checkout but weren’t clearly communicated earlier are a major violation. Common examples include:
- Payment processing fees.
- Vague or misleading shipping charges.
- Prices that don’t include VAT.
- Pricing errors caused by misconfigured store systems.
- To stay compliant, make sure all costs are clearly disclosed before the customer starts the checkout process.
5. Misleading Product Descriptions or Claims
Marketing content that includes unverified or exaggerated claims can lead to suspension.
To avoid this:
- Make sure your product descriptions are accurate and transparent.
- Any claim like “instant results” or “guaranteed improvement” should be backed by credible evidence, such as clinical studies.
6. Technical Issues During Checkout or Payment
Any issue that interrupts the buying process or raises concerns about your store’s reliability — such as:
- Errors in the shopping cart
- A confusing or poorly designed user interface
- Difficulties completing a purchase
— can lead to lost sales and reduced customer trust. Make sure the entire checkout experience is smooth, intuitive, and error-free. Pay attention to these details:
- Guest checkout: You can require users to sign up, but it should be quick, free, and not force them to download an app.
- Private customers: Allow purchases without requiring business info like a tax ID or company name. These fields should be optional.
- Product availability: Items marked “in stock” must actually be available for purchase.
- Order minimums: If you have a minimum order value, clearly state it in your shipping policy.
- Guest access: Let users check out as a guest, or with simple verification like an email or SMS code.
7. Missing or Incorrectly Implemented SSL Certificate
Your website must use HTTPS encryption — not just on the homepage, but especially during checkout and payment.
Missing or expired SSL certificates are considered a serious security issue.
8. Broken Links or Page Errors
Links that lead to a 404 error or non-functioning pages — whether it’s your terms and conditions, privacy policy, product pages, or images — can undermine your store’s credibility.
Ensure that all pages load correctly and that every essential section of your site is fully accessible.
9. Missing or Incomplete Legal and Contact Information
Your store’s website must clearly display:
- A valid phone number,
- Company address,
- Email contact,
- Full legal company details (including VAT or tax ID),
- Terms & Conditions,
- Privacy Policy,
- Shipping and return information.
Leaving out any of the above could cause Google to question your store’s legitimacy.
10. Mismatch Between Store Name and Registered Business Name
It’s common for a brand name (what users see) to differ from the official business name (what’s registered). That’s okay—as long as you communicate it clearly.
How to avoid issues:
- State the business owner clearly on your site (footer, terms, privacy policy, checkout documents).
- Match the business name in Merchant Center with what’s shown on your website and in your legal documents.
Here’s an example how it’s typically handled by well-known online stores:
- Reserved (clothing brand) is operated by “LPP S.A.”
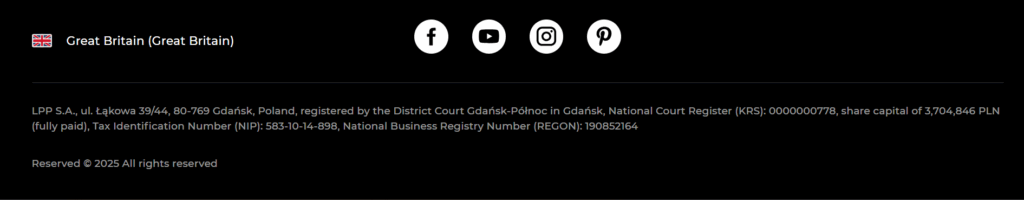
The same details have also been outlined in the store’s terms and conditions.
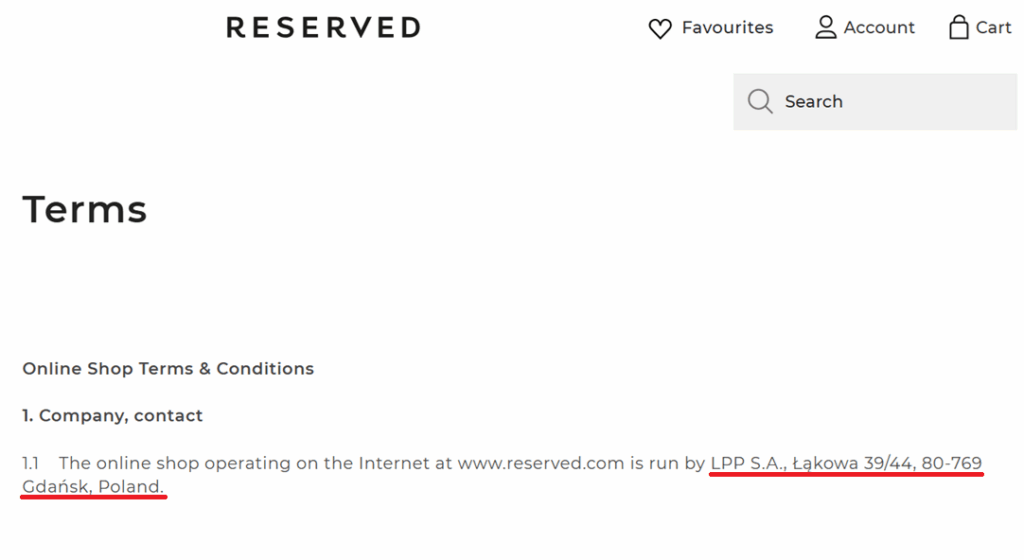
The privacy policy page should also include the correct company name and address.
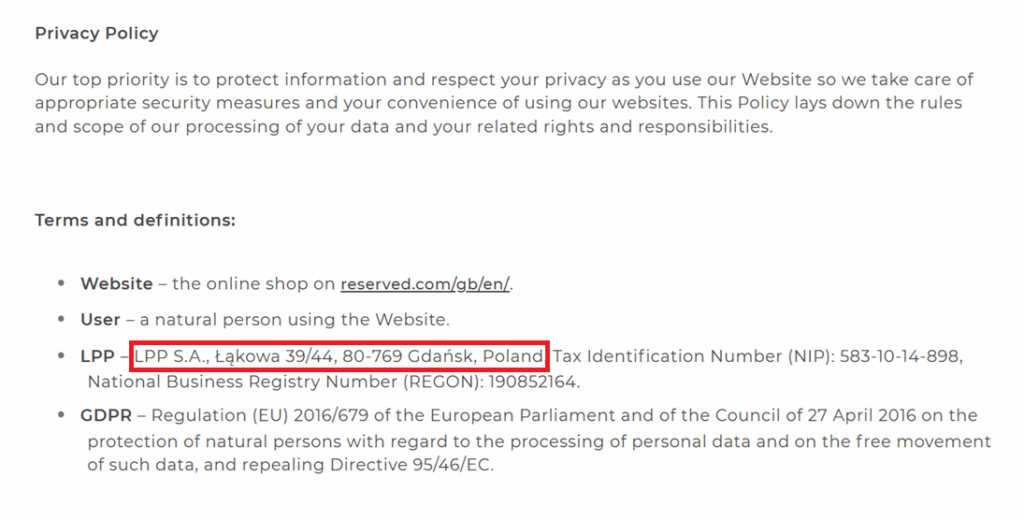
Consistency helps build trust—with users and Google.
Setting your business name in Merchant Center
Using an inappropriate or misleading business name can also potentially lead to account suspension. When adding your business name in Google Merchant Center, keep it simple and professional.
Do:
- Use a short, clean name—ideally your brand or domain name.
- Avoid suffixes like “LLC,” “Ltd.,” or “Inc.”
Don’t:
- Include phone numbers or promotions.
- Write in all caps or add emojis.
- Use personal names or private email addresses.
- Include offensive or inappropriate language.
11. Legal Compliance Issues – Omnibus Directive & Cookie Consent
Lowest price in the last 30 days
When offering a discount, EU law requires you to display the lowest price the item had in the past 30 days. Not doing so may be considered deceptive.
Customer reviews
If your site displays product or store reviews, you must disclose how you verify their authenticity (e.g., “only from verified buyers”). Unverified reviews can be seen as misleading.
Cookie consent
Your cookie banner must:
- Clearly explain what data you collect.
- Allow users to accept only essential cookies.
- Inform users if tools like Google Ads or Google Analytics are used.
If you use Google tools and a user declines marketing cookies, you must honor that via Google Consent Mode. Failing to implement it can violate policies.
12. Language and Currency Inconsistencies
The language and currency in your product feed must match:
- The language used on the site
- The language and settings in your Merchant Center account
If you sell in multiple countries:
- Use separate product data feeds for each language and market.
- Link to landing pages in the same language as the feed.
- Keep currency consistent throughout the entire checkout process.
13. Other Reasons for Suspensions
While these reasons may be less common based on our experience working with Google Ads and as a Comparison Shopping Service provider, they are equally important to address. Even if they occur less frequently, overlooking them can put your Merchant Center account at risk.
- Irrelevant landing pages: Ads must point to relevant, product-specific pages—not general or vague ones.
- Misusing product titles or images: Don’t add extra text in product titles or use images with promotional banners or distracting content.
- Placeholder content or incomplete pages: Avoid “coming soon” text, non-functional links, or default template elements.
- Dangerous domains: If your domain is hacked or flagged by Google as unsafe, it may block your ads and suspend your account.
- Duplicate or incomplete product details: Every product must have unique, accurate titles, descriptions, and images. Avoid generic or repeated info.
- Lack of transparency in charity or political campaigns: Disclose who’s behind the cause, how donations are handled, and the legal status of the organization.
- Illegal or policy-violating content: Laws vary by country, but Google generally prohibits ads for:
- Illegal products (e.g., unauthorized alcohol sales)
- Phishing and impersonation
- Misinformation (health, elections, climate change)
- Health misinformation: You must not promote dangerous health theories, deny the existence of diseases like COVID-19, or encourage treatments that contradict established medical knowledge.
- False information about elections and democracy: Avoid spreading untrue claims about voting processes, candidates, election results, or fake news about public figures.
- Climate change denial: Don’t publish content that contradicts widely accepted scientific consensus on global warming.
Want to learn more about Google’s misrepresentation policy?
Official Google Support Page
Google Product Ads Policies – What You Should Know
Google has created a set of policies for product ads to ensure user safety, message transparency, and legal compliance. Every product ad—whether in Google Shopping or Local Inventory Ads—must follow these rules:
- Counterfeit Products
- Promoting fake goods that imitate well-known brands is strictly prohibited. This includes fake logos, names, or packaging that could mislead users.
- Dangerous Products
- You’re not allowed to advertise items that could harm users, such as firearms, fireworks, explosives, or guides on how to make them.
- Healthcare and Medicines
- Google restricts or bans the promotion of pharmaceuticals (prescription and over-the-counter), dietary supplements, medical devices, and treatments that lack proven effectiveness.
- Inappropriate Content
- Nudity, violence, hate speech, shocking, or offensive content is not allowed in any form.
- Products Enabling Dishonest Behavior
- Google bans advertising tools used for deception—like credit card skimmers, fake documents, hacking tools, or devices that bypass security systems.
- Trademark Violations
- Using brand names or logos in a way that infringes on the trademark owner’s rights may lead to ad disapproval or legal consequences.
- Copyrighted Content
- You cannot promote content that violates copyright laws—this includes pirated movies, music, or software.
- Alcohol
- Advertising alcohol is allowed only in countries where it’s legally permitted—and must comply with Google’s local ad policies, including content and audience targeting restrictions.
More info on Google’s Product Ads policies:
Google Support – Product Data Policies
Product Attributes
These basic attributes must be provided for every product, regardless of the industry, target country, or campaign type. Without them, your listings won’t be approved or shown in paid or free listings:
- id – product ID,
- title or structured_title,
- description or structured_description,
- link – product landing page URL,
- image_link – main product image,
- availability – in stock, out of stock, etc.,
- availability_date – when the product will become available (if applicable),
- price – product price.
Attributes Required in Specific Cases
Depending on the nature of your offer, Google may require additional information—especially for apparel, used items, bundles, or digital goods. These include:
- brand – Required for all new products except movies, books, and music,
- gtin – Global Trade Item Number, if available,
- mpn – Manufacturer Part Number, if GTIN is not assigned,
- condition – Required for used or refurbished products,
- adult – If the product includes adult content,
- shipping – Required in countries like Australia, Austria, Belgium, Czechia, France, Germany, India, Ireland, Israel, Japan, Canada, South Korea, Netherlands, New Zealand, Poland, Romania, Spain, Switzerland, UK, and the US,
- material – Required if used to differentiate variants,
- pattern – Required if relevant to distinguishing variants,
- certification – For products that must display certification info due to local laws (e.g., energy labels),
- age_group – For all products targeting specific age groups and for all apparel in Brazil, France, Germany, Japan, UK, and US,
- multipack – Required for multipacks sold in Australia, Brazil, Czechia, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, Spain, Switzerland, UK, and US,
- is_bundle – For product bundles in the same countries listed above,
- color – Required for variants and apparel sold in Brazil, France, Germany, Japan, UK, and US.
- gender – Required for gender-specific products and all apparel in Brazil, France, Germany, Japan, UK, and US.
- size – Required for size-specific products and apparel in categories like “Clothing & Accessories > Clothing” and “Clothing & Accessories > Shoes,” in the countries mentioned above,
- item_group_id – Required if you sell product variants in Brazil, France, Germany, Japan, UK, and US,
- external_seller_id – Needed if you’re operating a marketplace and using a multi-seller account,
- tax – Required in the United States only.
Want full details? Check out the official documentation:
Google Support – Product Attributes
Requesting a Review of Your Store by Google
If you’ve identified and successfully fixed all policy violations, you can submit your account for a review. This step is essential to restore your ability to run product ads.
However, before you do, make sure your website is thoroughly prepared and all potential issues have been addressed. The number of review requests you can submit is limited, and misusing them could lead to permanent suspension of your store.
If you believe the suspension was a mistake, you can still request a review. That said, we strongly recommend conducting a thorough audit of your account before submitting an appeal.
Before You Appeal
Before submitting your store for a review, consider these important steps:
- Check and fix all possible causes of the suspension—even if Google’s notifications aren’t fully detailed, it doesn’t mean there isn’t an underlying problem.
- Use a checklist (for example, the one in this guide) to ensure your store meets Google’s technical, legal, and policy requirements.
- Don’t rush to submit a review request—each appeal should be backed by a full audit and necessary fixes, as the number of appeals is limited.
If Google finds unresolved violations after your review request, you’ll see a warning like this:
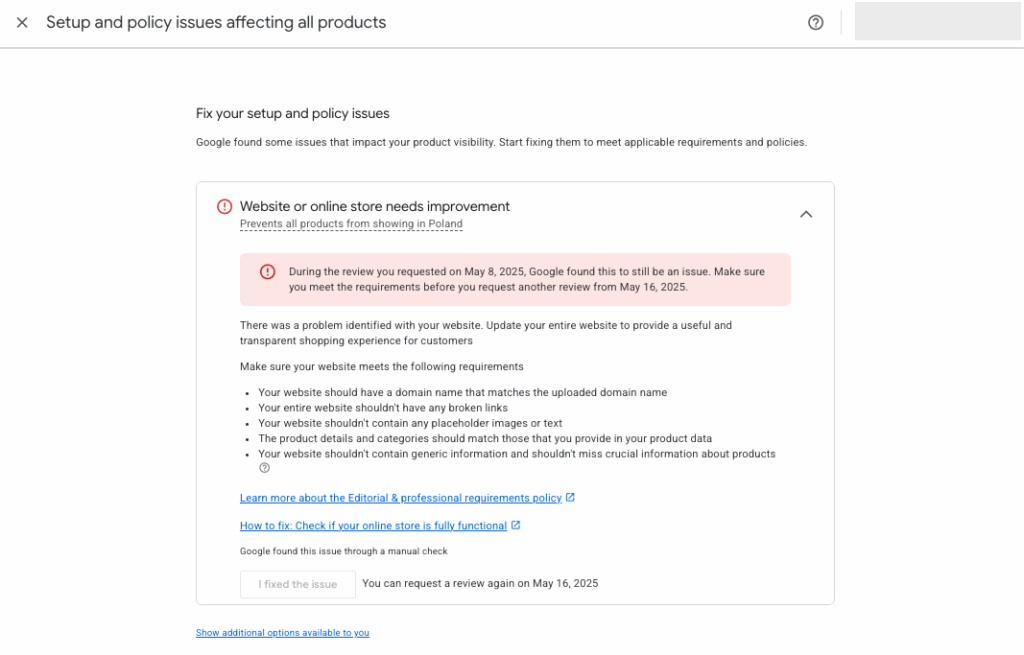
⚠️ Beware of the “Final Review Request” Warning
Before submitting the form, check if your Merchant Center account shows a “final review request” notification. If you see this message:
- After your request is rejected, you won’t be able to submit any further appeals.
- Your account will be permanently suspended—your store won’t be able to advertise via Google Merchant Center anymore.
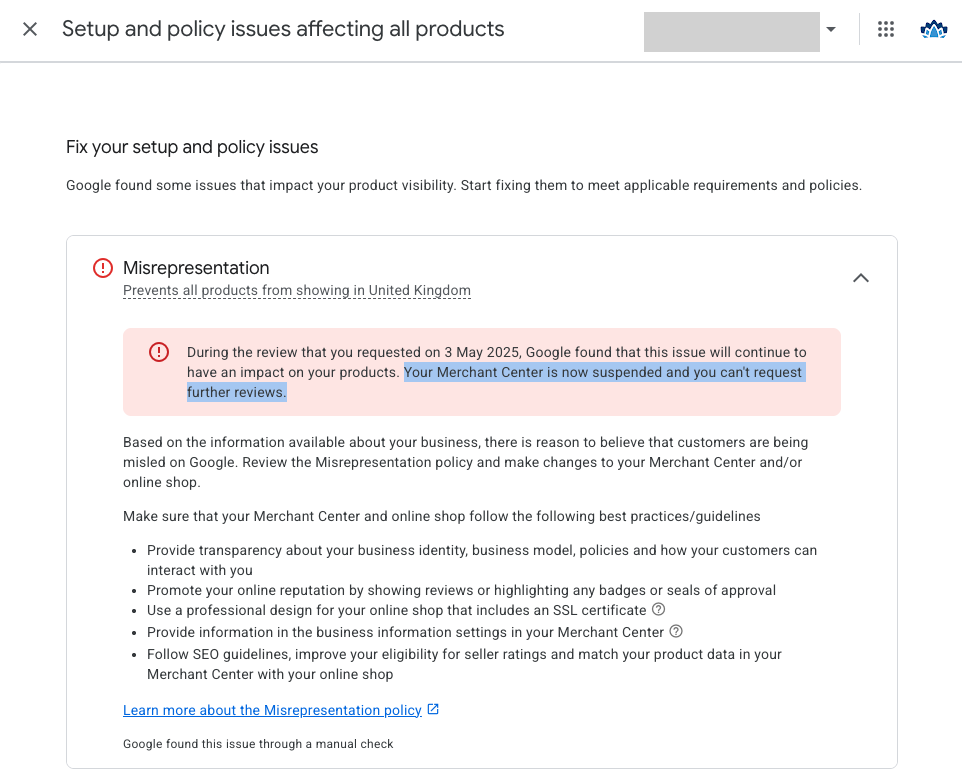
Submitting a review request before fully fixing all issues can result in irreversible account suspension. In that case, there will be no way to restore your product visibility in Google Ads using the same store domain.
Solving the Google Merchant Center Misrepresentation Issue
If Google finds no policy violations during the follow-up review, your account will be reinstated and your ads will start running again.
Keep in mind, though, that reinstatement is not the end of the process. Google may conduct periodic checks, so it’s crucial to continuously maintain compliance, keep your website and product data high quality, and provide a transparent and positive shopping experience. These are key to keeping your account active in the long term.
Following a successful review, Google will inform you of the approval via email. Additionally, you’ll see the updates directly in your Merchant Center dashboard.
Once your account is fully compliant and ready to advertise again, make the most of your Shopping Ads by lowering costs.
💡 By switching to a Google-approved Comparison Shopping Service like Sellie CSS, you can lower your cost-per-click by up to 20% — without changing your campaigns or product data.
🚀 Ready to boost your performance and save on clicks? Get in touch with us and see how easy it is to switch to Sellie CSS.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can I just create a new Merchant Center account instead of fixing the current one?
No. A misrepresentation suspension is tied to your store’s domain (URL), not just the account itself. Therefore, creating a new Merchant Center account — even with a different email address or CSS ID — won’t solve the issue. The new account will likely get suspended as well.
Is switching to another CSS a way to fix Google Merchant Center suspension?
No. Changing your CSS provider doesn’t affect your store’s quality evaluation or reset any past violations. If the root issue (e.g. incorrect information on your website) isn’t fixed, the suspension will remain active regardless of which CSS model you use.
Will Google support clearly tell me what’s wrong with my store?
Usually not. In our experience, Google Merchant Center support rarely provides specific reasons for suspensions. Instead, the messages tend to be generic and refer broadly to “policy violations.” It’s still worth reaching out to Google Ads support, which can sometimes be more responsive and offer some guidance—though don’t expect a full diagnosis there either.
Final Thoughts: Google Merchant Center Misrepresentation Issue
Fixing your Google Merchant Center suspension for misrepresentation is crucial to restore your product visibility on Google and getting your ads back online. Although Google’s notifications are often vague, the most common causes are discrepancies in product data or failing to meet transparency requirements.
In this article, we covered not only the 12 most common reasons for suspensions but also other important factors—like technical, legal, and product data requirements. Identifying and fixing all potential violations is key to regaining compliance with Google’s policies.
Before submitting your account for review, make absolutely sure you’ve resolved every issue. Since the number of appeals is limited, rushing can lead to permanent suspension. A thorough audit and accurate data are your best bet to successfully restore your ability to advertise on Google.
Click to reveal useful resources from Google Support
To help you get the most out of your Google Ads campaigns, consider using Sellie CSS.
💸 Save more and achieve better results with this powerful tool — discover the benefits!
